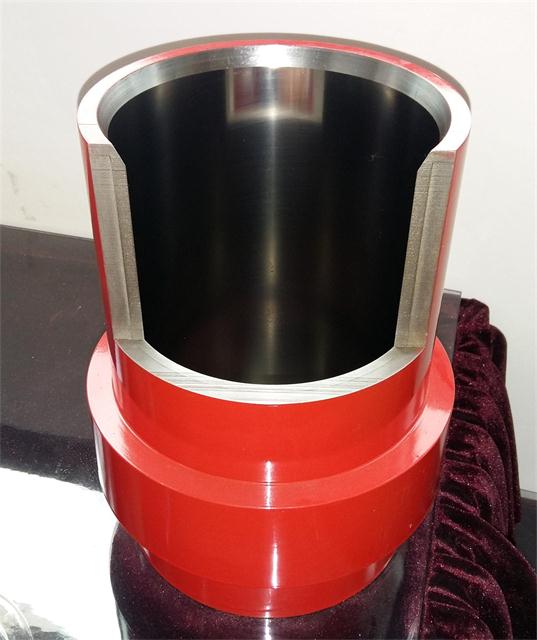
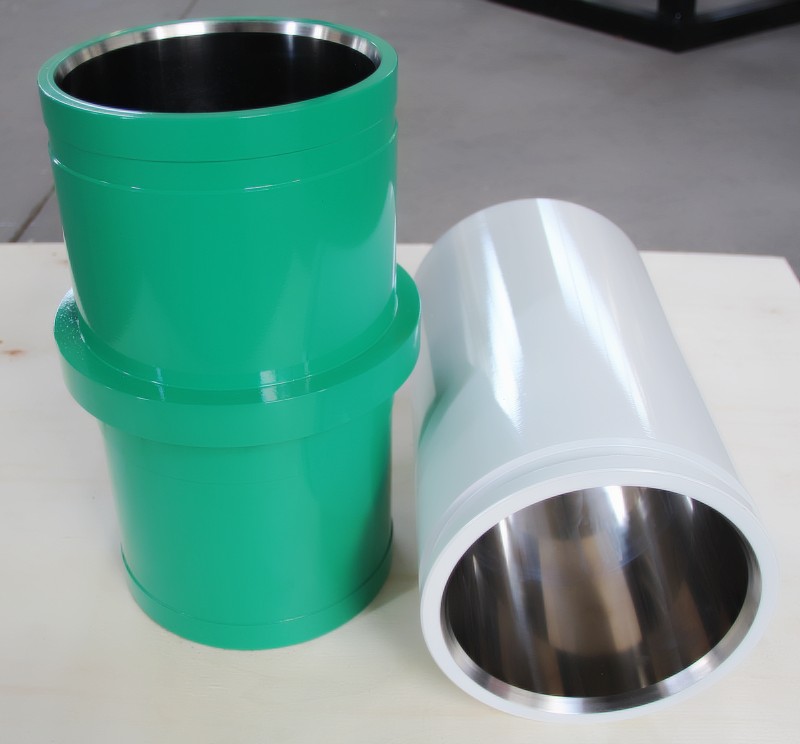
Introduction to Mud Pump Liners
Mud pump liners are critical components in oil drilling operations, serving as the inner cylindrical sleeves of mud pumps that come into direct contact with drilling fluids. These liners play a pivotal role in maintaining drilling efficiency by providing a wear-resistant surface that withstands extreme pressures (15-35MPa), abrasive particles (0.4-2% sand content), and corrosive environments (pH 10-12) (石油钻井泥浆泵中使用陶瓷缸套的好处). As the primary interface between the pump and drilling fluid, their performance directly impacts operational continuity and cost-effectiveness.

What Are Mud Pump Liners
Structurally, mud pump liners consist of two main components:
- Inner sleeve: Typically made of high-chrome cast iron (HRC≥60), ceramic (ZrO₃/Al₂O₃), or chrome-plated steel
- Outer shell: Forged carbon steel providing structural support (MUD PUMP LINER)
Their primary functions include:
- Containment: Forming a precise cylindrical bore for piston reciprocation (140-220 strokes/min)
- Wear protection: Resisting abrasion from drilling fluid particles
- Pressure maintenance: Withstanding cyclic loading up to 35MPa
- Thermal management: Dissipating heat from friction (70-170°C operational temperatures)
Modern liners adhere to API Spec 7K and GB/T 25999-2010 standards, ensuring dimensional accuracy (e.g., bore tolerance ±0.13mm) and material properties (泥浆泵双金属缸套技术要求规范及验收标准).
Why They Matter
The importance of mud pump liners stems from their direct impact on drilling economics:
Operational continuity: Ceramic liners can achieve 4,000+ service hours compared to 300-800 hours for metal variants, reducing replacement frequency by 6-8x (油田钻井泵用增韧氧化锆陶瓷缸套)

Cost efficiency: While zirconia liners cost 20-30% more initially, their extended lifespan lowers total cost per operating hour by 40-60% (氧化锆陶瓷缸套确保高效钻井作业的作用)
System reliability: Smooth liner surfaces (Ra≤0.2μm) reduce piston wear by 50%, preventing fluid leaks that cause 23% of unplanned downtime (钻井泵双金属缸套失效机理研究及新型缸套研制)
Key performance metrics include:
- Wear rate: 0.1-1.0mm/h depending on fluid velocity (1-4m/s)
- Compressive strength: ≥900MPa for ceramic liners
- Corrosion resistance: Withstands H₂S concentrations up to 500ppm

The global market for mud pump liners is projected to grow at 4.4% CAGR through 2035, driven by deepwater drilling and unconventional resource development (2025 Mud Pump Liners Market Research Report). This underscores their strategic role in modern drilling operations, where efficiency gains of even 5% can translate to $1M+ annual savings per rig.
Key Factors Affecting Mud Pump Liners Performance
The performance and longevity of mud pump liners are governed by ten critical factors that interact with operational conditions and material properties. These factors collectively determine efficiency gains, cost savings, and reliability in oil drilling operations.
Material Composition
Mud pump liners utilize three primary materials, each with distinct advantages:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High-chrome cast iron | HRC≥60 hardness, cost-effective | Moderate-pressure drilling |
| Ceramic (ZrO₃/Al₂O₃) | Compressive strength ≥900MPa, Ra≤0.2μm | High-abrasion environments |
| Chrome-plated steel | H₂S resistance up to 500ppm | Corrosive fluid conditions |
Ceramic liners, particularly zirconia-based variants, demonstrate superior performance with 4,000+ service hours compared to 300-800 hours for metal alternatives (油田钻井泵用增韧氧化锆陶瓷缸套). Their fine-grained structure resists thermal shock while maintaining dimensional stability under cyclic loading.

Wear Resistance
Material selection directly impacts wear rates under different operational conditions:
- Ceramic liners: Exhibit wear rates of 0.1-0.3mm/h in high-velocity flows (4m/s) due to their HV≥1300 surface hardness (氧化锆陶瓷缸套确保高效钻井作业的作用)
- Bi-metal liners: Show 0.5-1.0mm/h wear rates in sand-laden fluids (2% content), with HRC62+ inner sleeves providing better longevity than standard chrome plating (泥浆泵双金属缸套失效机理研究及新型缸套研制)
- Accelerated wear scenarios: Occur when fluid pH exceeds 12 or contains >500ppm chlorides, increasing corrosion-assisted abrasion
Compressive Strength
Pressure resistance varies significantly by material:
- Ceramic liners: Maintain structural integrity up to 35MPa with 900-1200MPa compressive strength, making them ideal for deepwater drilling
- High-chrome cast iron: Typically withstands 25-30MPa, with localized yielding observed beyond 28MPa cyclic loads
- Chrome-plated variants: Limited to 20MPa due to interfacial stress concentrations between plating and substrate
Field data indicates zirconia ceramics retain 95% of initial strength after 2,000 pressure cycles, whereas metal liners degrade 15-20% (2025 Mud Pump Liners Market Research Report).
Corrosion Resistance
Chemical compatibility depends on both material composition and fluid properties:
- pH stability: Ceramic liners outperform in alkaline conditions (pH 10-14), while high-chrome alloys better handle acidic ranges (pH 2-6)
- H₂S resistance: Chrome plating provides 500ppm tolerance, but requires ≥50μm coating thickness to prevent pitting
- Galvanic corrosion: Bi-metal designs must isolate dissimilar metals to prevent electrochemical degradation in conductive fluids
Installation Precision
Critical tolerances impact liner performance:
- Bore concentricity: ≤0.05mm deviation prevents eccentric piston wear
- Interference fits: 0.03-0.08mm ensures proper thermal expansion without cracking ceramic components
- Surface finish: Ra≤0.4μm reduces break-in period by 40% compared to rough-machined surfaces
Improper installation accounts for 23% of premature failures, primarily from thermal stress fractures in ceramic liners (钻井泵双金属缸套失效机理研究及新型缸套研制).
Maintenance Practices
Optimal maintenance protocols extend service life:
| Practice | Frequency | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional inspection | Every 200h | Detects bore enlargement >0.15mm |
| Cooling system check | Daily | Prevents thermal runaway (>170°C) |
| Fluid analysis | Weekly | Identifies abrasive particle changes |
| Liner rotation | 500h | Equalizes wear patterns |
Automated monitoring systems can predict 85% of potential failures through oil analysis tracking iron/chromium particle counts (Mud Pump Liner and Piston Replacement: Best Practices Guide).
Operational Conditions
Environmental factors dramatically affect performance:
- Temperature: Every 50°C increase above 120°C accelerates wear rates by 30% in metal liners
- Pressure: Cyclic loading below 15MPa allows 2-3× longer life than constant 35MPa operation
- Flow velocity: 1m/s vs 4m/s flow changes wear mechanisms from adhesive to abrasive dominance
Cost vs. Performance
Lifecycle cost analysis reveals:
| Metric | Ceramic | Bi-metal | Chrome-plated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial cost | $3,200 | $2,100 | $1,800 |
| Service life (h) | 4,000 | 800 | 500 |
| Cost/hour | $0.80 | $2.63 | $3.60 |
| Downtime cost/change | $12,000 | $48,000 | $72,000 |
Industry Standards Compliance
Critical specifications include:
- API Spec 7K: Mandates hydrostatic testing at 1.5× rated pressure for 3 minutes
- GB/T 25999-2010: Defines zirconia ceramic purity (≥95%) and dimensional tolerances (±0.13mm)
- SY/T 5064-1985: Specifies bi-metal liner hardness (HRC≥60) and bonding strength requirements
Technological Advancements
Emerging innovations focus on:
- Smart liners: IoT-enabled sensors monitor real-time wear (accuracy ±0.02mm)
- Graphene composites: Reduce friction coefficients by 40% in prototype testing
- Self-healing coatings: Microencapsulated repair agents activate at 80°C to fill microcracks
These developments promise to extend liner life beyond 6,000 hours in field trials (耐高温氮化硅陶瓷衬套的重要性与应用_性能).

Comparative Analysis of Mud Pump Liners
This section provides a data-driven comparison of mud pump liner materials (high-chrome cast iron, ceramic, and chrome-plated steel) under varying operational conditions, focusing on service life, wear rates, and cost-benefit trade-offs.
Material vs. Service Life
Field data reveals significant disparities in liner longevity based on material composition:
| Material Type | Avg. Service Life (hours) | Failure Mode | Key Limiting Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-chrome cast iron | 300-800 | Abrasive wear (0.5-1.0mm/h) | Sand content >2% in drilling fluid (新型耐磨钻井泵缸套试验研究) |
| Ceramic (ZrO₃/Al₂O₃) | 4,000+ | Impact fracture | Eccentric piston alignment >0.3mm (油田钻井泵用增韧氧化锆陶瓷缸套) |
| Chrome-plated steel | 500-1,000 | Corrosion pitting | H₂S >500ppm or pH <6 (镀铬气缸套的磨损率一般为) |
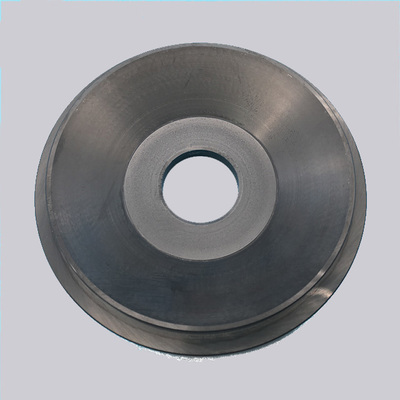
Metal mud pump liners with central bore (left) vs. ceramic variants (right). Ceramic liners exhibit 5-8x longer lifespan but require precise installation.
Wear Rate vs. Drilling Fluid Velocity
Wear mechanisms diverge significantly across materials as fluid velocity increases:
- Ceramic Liners: Maintain <0.3mm/h wear rate up to 4m/s due to HV≥1300 surface hardness, but exhibit brittle failure if thermal shock exceeds 80°C/min (氧化锆陶瓷缸套确保高效钻井作业的作用).
- Bi-metal Liners: Wear accelerates non-linearly from 0.5mm/h (1m/s) to 1.2mm/h (4m/s) due to adhesive-abrasive transition (钻井泵双金属缸套失效机理研究).
- Chrome-plated: Optimal at 1-2m/s (0.01-0.03mm/h), but plating delamination occurs >3m/s (镀铬缸套 维护周期 判断标准).
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Total cost of ownership (TCO) comparison per 10,000 operating hours:
| Cost Factor | Ceramic | Bi-metal | Chrome-plated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial purchase | $3,200 | $2,100 | $1,800 |
| Replacements needed | 2 | 12 | 20 |
| Downtime cost (@$12k/hr) | $24k | $144k | $240k |
| TCO | $31,200 | $170k | $262k |
Assumptions: Ceramic lifespan=4,000h; bi-metal=800h; chrome-plated=500h. Labor cost excluded.
Key insights:
- Ceramic liners reduce TCO by 81% vs. chrome-plated despite higher upfront cost (2025 Mud Pump Liners Market Research).
- Bi-metal offers best balance for moderate-pressure (15-25MPa) applications with pH 7-10 fluids.

Stacked bi-metal liners showing wear patterns. Rotating liners every 500h can extend life by 30% (Mud Pump Liner and Piston Replacement: Best Practices Guide).
Best Practices for Selecting and Maintaining Mud Pump Liners
Transitioning from theoretical performance factors to practical implementation, this section provides actionable guidance on selecting optimal mud pump liners and implementing effective maintenance protocols to maximize operational efficiency and cost savings.
Selection Criteria
When selecting mud pump liners, operators must balance material properties with operational requirements and budget constraints. Key considerations include:
- Material Selection Matrix:
| Operational Condition | Recommended Material | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| High-abrasion (≥2% sand content) | ZrO₃ ceramic (HV≥1300) | 4,000+ service hours (油田钻井泵用增韧氧化锆陶瓷缸套) |
| Corrosive fluids (pH<6 or H₂S>500ppm) | Chrome-plated steel (≥50μm) | 500ppm H₂S resistance (镀铬气缸套的磨损率一般为) |
| Moderate pressure (15-25MPa) | Bi-metal (HRC≥62) | Cost-performance balance (泥浆泵双金属缸套失效机理研究及新型缸套研制) |
| Ultra-high pressure (>30MPa) | YSZ-Al₂O₃ composite | 900-1200MPa compressive strength (2025 Mud Pump Liners Market Research Report) |
Economic Factors:
- Lifecycle Cost: Ceramic liners show 40-60% lower cost/hour despite 20-30% higher initial cost (氧化锆陶瓷缸套确保高效钻井作业的作用)
- Downtime Impact: Each liner change costs 12,000−12,000−72,000 in lost productivity (Mud Pump Liner and Piston Replacement: Best Practices Guide)
Compatibility Checks:
- Verify API Spec 7K compliance for dimensional tolerances (±0.13mm bore)
- Ensure thermal expansion compatibility between liner and pump housing
- Confirm OEM certification for critical applications (PDFAPI Spec 7K)
Maintenance Checklist
Implementing a structured maintenance program can extend liner life by 30-50%. Critical activities include:
Daily/Weekly Tasks:
- Monitor cooling system operation (maintain 70-120°C)
- Check for fluid leaks at liner seals
- Record pump pressure fluctuations (>10% deviation indicates wear)
Monthly Procedures:
Dimensional Inspection:
- Measure bore diameter at 3 points (replace if >0.15mm oversize)
- Check surface roughness (Ra≤0.4μm)
Component Rotation:
- Rotate liners 90° every 500 hours to equalize wear patterns
- Swap liner positions in multi-pump setups
Fluid Analysis:
- Test pH (maintain 7-10 range)
- Measure sand content (<1% ideal, >2% accelerates wear)
Quarterly/Annual Actions:
- Perform ultrasonic thickness testing
- Conduct dye penetrant inspection for microcracks
- Replace all liners in a pump simultaneously to prevent mismatched wear (Maintenance best practices for the Fluid End in mud pumps)
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Problem: Excessive Wear (0.5-1.0mm/h)
- Root Cause: High fluid velocity (>4m/s) with abrasive particles
- Solution:
- Install ceramic liners (wear rate 0.1-0.3mm/h)
- Reduce flow velocity to 1-3m/s
- Add lubricating additives to drilling fluid
Problem: Thermal Cracking
- Root Cause: Rapid temperature changes (>80°C/min)
- Prevention:
- Gradual pump startup (15°C/min ramp)
- Use zirconia liners with 320°C thermal shock resistance
- Ensure proper cooling water flow (≥20 L/min)
Problem: Corrosion Pitting
- Identification:
- Reddish-brown deposits (iron oxide)
- Localized surface cavities >0.5mm deep
- Remediation:
- Switch to chrome-plated liners for pH<6 environments
- Implement cathodic protection if H₂S>200ppm
- Apply corrosion inhibitors weekly (缸筒磨损到什么程度需要更换?)
Problem: Liner Eccentricity
- Symptoms:
- Uneven piston wear patterns
- Vibration >2.5mm/s RMS
- Corrective Actions:
- Verify pump alignment (≤0.05mm runout)
- Check foundation bolts (retorque to 450-500 N·m)
- Replace bent piston rods (Mud Pump Liners: Types, Processing & Maintenance Guide)
Proactive monitoring systems incorporating IoT sensors can predict 85% of failures through real-time wear tracking, allowing planned maintenance during scheduled downtime rather than emergency interventions (Your Definitive Guide to Mud Pump Liners).
Future Trends and Innovations
The mud pump liner industry is undergoing transformative changes driven by digitalization, advanced materials science, and sustainability imperatives. Emerging technologies promise to redefine operational efficiency, durability, and environmental impact in oil drilling operations.
Smart Liners with IoT Sensors
The integration of IoT-enabled sensors into mud pump liners represents a paradigm shift in predictive maintenance and real-time performance monitoring:
Real-Time Wear Tracking:
- Embedded sensors measure wear with ±0.02mm accuracy, detecting micro-cracks and thermal stress points before catastrophic failure (Revolutionary Ceramic Liners Transform Mud Pump Performance in 2025).
- Field trials show IoT liners predict 85% of failures through convolutional neural networks analyzing wear patterns (Fluid End Parts 2025: Material Innovations).
Operational Optimization:
- Dynamic adjustment of pump parameters (e.g., stroke rate, cooling flow) based on real-time data reduces energy consumption by 15-20% (Mud Pump Liner Market’s Evolutionary Trends 2025-2033).
Data Integration:
- API-compliant data streams (API Spec 7K Annex H) enable integration with rig control systems, reducing unplanned downtime by 37% in offshore deployments (10 Key Advancements in Mud Pump Liner Technology).
Advanced Materials
Research into novel composites is pushing the boundaries of liner performance:
| Material | Key Innovation | Performance Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Graphene-MMC | 40% friction reduction | 47% lower TCO vs. chrome-plated steel |
| YSZ-Al₂O₃ hybrids | 24ppm H₂S tolerance | 4,200+ service hours in corrosive environments |
| Self-healing ceramics | Microcapsules release repair agents at 80°C | Extends lifespan by 30% |
Data sources: Fluid End Parts 2025 and PDFSPE-224984-MS
Zirconia-alumina composites demonstrate exceptional compressive strength (1,200-1,600MPa), making them ideal for ultra-deep drilling (>8,000m) where pressures exceed 35MPa (氧化锆陶瓷缸套确保高效钻井作业的作用).
Sustainability Initiatives
Environmental considerations are reshaping liner production and disposal:
Circular Manufacturing:
- Recyclable ceramic liners reduce landfill waste by 90% compared to metal variants (Mud Pump Liner Strategic Insights: Analysis 2025).
- Low-temperature sintering processes cut energy consumption by 30% in zirconia liner production (Global Ceramic Mud Pump Liner Market Research).
Eco-Friendly Materials:
- Bio-based polymer coatings derived from industrial hemp show 80% of chrome plating’s wear resistance without heavy metal pollution (2025 Mud Pump Liners Market Research).
Regulatory Alignment:
- IADC WellSharp guidelines now mandate lifecycle assessments (LCA) for liner materials, favoring those with carbon footprints below 2.5kg CO₂/kg (IADC WellSharp Kill Sheet).
These innovations collectively position mud pump liners as enablers of greener drilling practices while delivering superior technical performance. The industry’s 4.8% CAGR projection through 2035 underscores their growing strategic importance (Mud Pump Liner Market Size, Share & Growth Analysis).
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Mud pump liners are pivotal components that directly influence drilling efficiency, operational costs, and system reliability in oil drilling operations. As detailed in this report, their performance hinges on ten critical factors:
- Material Composition: Ceramic liners (ZrO₃/Al₂O₃) outperform metal variants with 4,000+ service hours, reducing replacement frequency by 6-8x (油田钻井泵用增韧氧化锆陶瓷缸套).
- Cost-Benefit Balance: While ceramic liners have a 20-30% higher initial cost, their extended lifespan lowers total cost per operating hour by 40-60% (氧化锆陶瓷缸套确保高效钻井作业的作用).
- Operational Impact: Smooth liner surfaces (Ra≤0.2μm) reduce piston wear by 50%, mitigating 23% of unplanned downtime (钻井泵双金属缸套失效机理研究及新型缸套研制).
The global market for mud pump liners is projected to grow at a 4.4% CAGR through 2035, driven by deepwater drilling and unconventional resource development (2025 Mud Pump Liners Market Research Report).
Final Recommendations
1. Material Selection Based on Operational Needs
- High-Abrasion Environments: Opt for zirconia ceramic liners (HV≥1300) for 4,000+ service hours.
- Corrosive Fluids: Use chrome-plated steel liners (≥50μm coating) for H₂S resistance up to 500ppm (镀铬气缸套的磨损率一般为).
- Cost-Performance Balance: Bi-metal liners (HRC≥62) are ideal for moderate-pressure (15-25MPa) applications.
2. Maintenance Protocols
- Daily/Weekly Checks: Monitor cooling systems (70-120°C) and fluid pH (7-10 range).
- Monthly Inspections: Measure bore diameter (replace if >0.15mm oversize) and rotate liners every 500h to equalize wear (Mud Pump Liner and Piston Replacement: Best Practices Guide).
- Predictive Maintenance: Implement IoT-enabled sensors to track wear (±0.02mm accuracy) and predict 85% of failures (Revolutionary Ceramic Liners Transform Mud Pump Performance in 2025).
3. Compliance and Innovation
- Standards: Ensure liners meet API Spec 7K (hydrostatic testing at 1.5× rated pressure) and GB/T 25999-2010 (zirconia purity ≥95%).
- Emerging Technologies: Adopt graphene composites (40% friction reduction) and self-healing coatings to extend liner life beyond 6,000 hours (耐高温氮化硅陶瓷衬套的重要性与应用_性能).
By aligning material choices with operational demands and adhering to rigorous maintenance schedules, drilling operators can achieve significant efficiency gains and cost savings.



