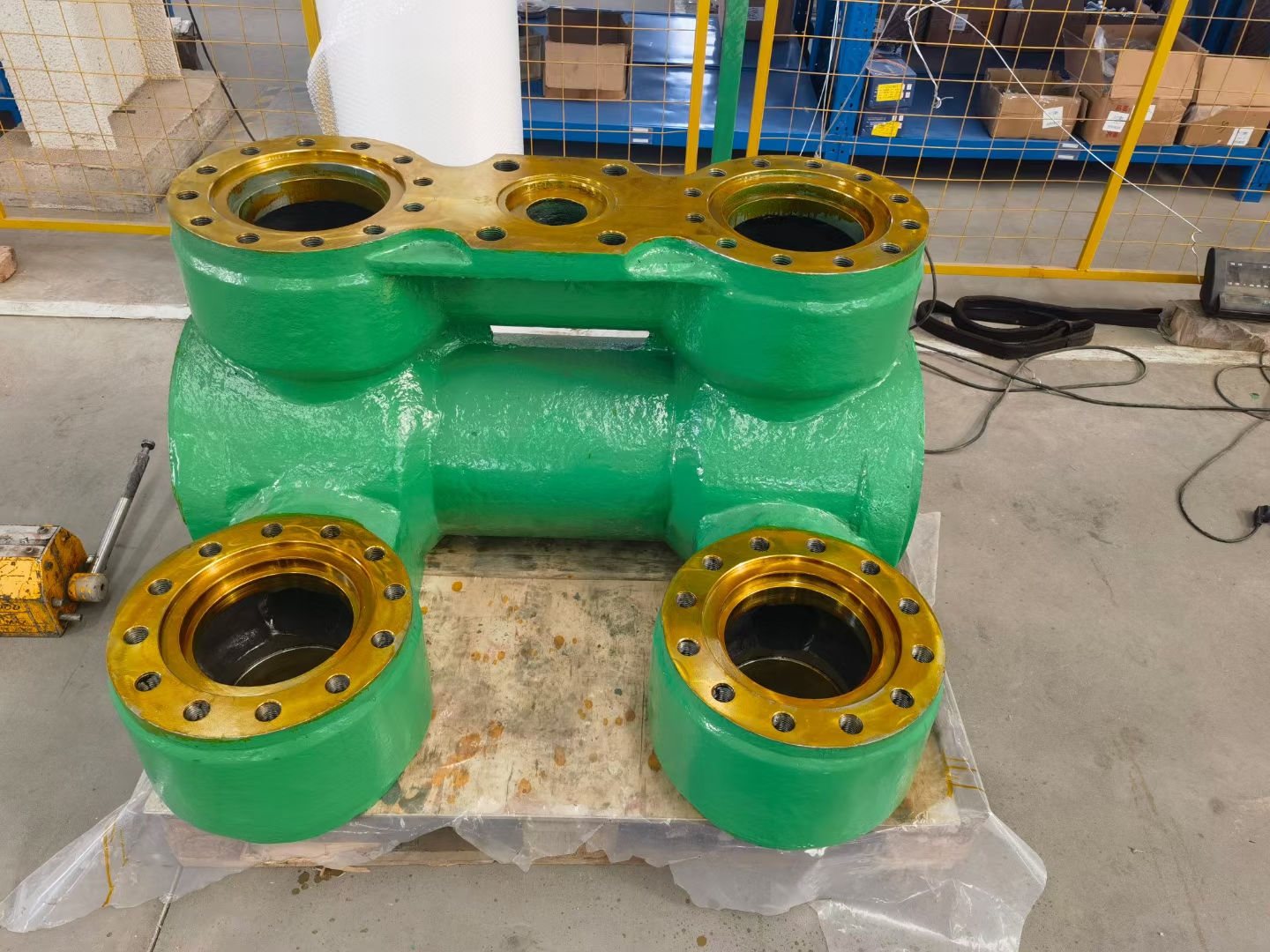
Mud Pump UNB600 fluid end module
Basic Composition and Function of Fluid End Module
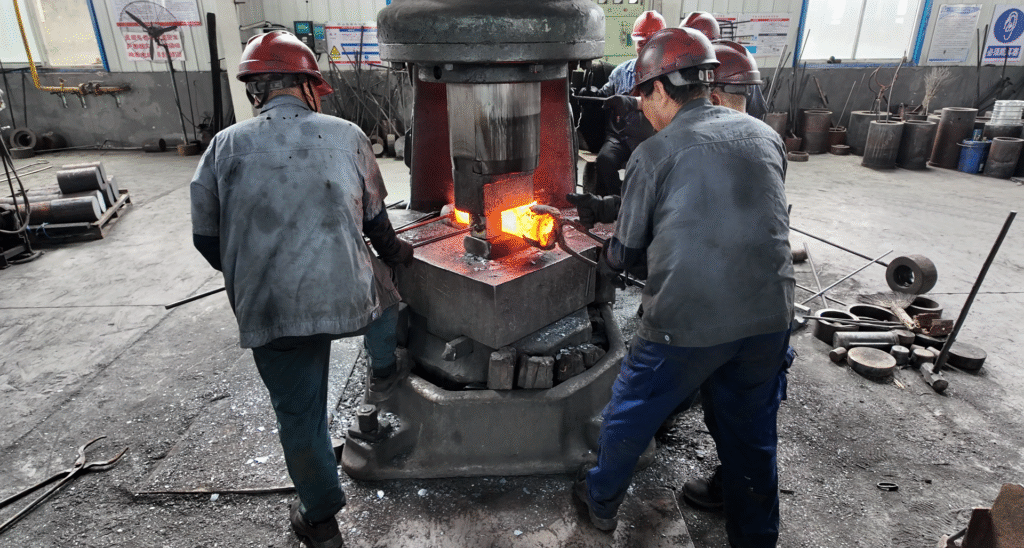
The fluid end module, also known as the valve box or hydraulic cylinder, is a major part of the mud pump’s fluid end parts. Its main function is to suck in and discharge the drilling fluid, and it is a key component for realizing the fluid conveying function of the mud pump 1. The typical fluid end module is blank forged by high – strength alloy steel, and after heat treatment and multi – channel processes, it has high strength and durability

Selling Points
- High Power and Versatility
- Interchangeable Components for Reduced Costs
- Durable Materials Ensuring Longevity
- Comprehensive Spare Parts Availability
Feature
- High-Strength Material Construction: The fluid end is typically forged from high-strength alloy steel and undergoes heat treatment to enhance durability and resistance to fatigue and corrosion [1].
- Precision Machining: Ensures tight tolerances and smooth internal surfaces to reduce turbulence and wear during operation.
- Interchangeable Components: Designed with modular and interchangeable parts such as cylinder liners, valves, seats, and plungers, which simplifies maintenance and reduces downtime [1].
- High Pressure and Flow Capacity: Optimized for high-pressure applications, making it suitable for deep and ultra-deep drilling operations.
Technical Specifications:
Parameter Description Model Compatibility UNB600 Material High-strength alloy steel, heat-treated Cylinder Liner Inner Diameter Available in multiple sizes (e.g., 60mm to 300mm) Type Fluid End Module (Valve Box) Application Oil & Gas Drilling, Mud Circulation System Design Standard Complies with API 7K and other international drilling equipment standards Working Pressure High-pressure capable (specific values depend on system configuration) Components Included Cylinder liners, valves, seats, plungers, fluid end housing Main Components of the Fluid End Module:
- Cylinder Liner: The inner sleeve where the piston or plunger reciprocates; available in different materials such as chrome-plated steel or hardened alloys for extended service life [1].
- Valve and Seat Assembly: Ensures unidirectional flow of drilling fluid and is made from wear-resistant materials.
- Plunger or Piston: Reciprocates inside the cylinder liner to generate pressure; often coated with materials like ceramic or polyurethane for abrasion resistance.
- Valve Box (Fluid End Housing): The main body that houses the cylinder liner, valves, and seats.
Applications:
- Drilling Rigs: Used in land and offshore drilling operations.
- Well Servicing Units: Applied in workover and completion operations.
- Fracturing Units: Integrated into high-pressure pumping systems for hydraulic fracturing.
Advantages:
- Durability: Engineered for long service life under harsh operating conditions.
- Easy Maintenance: Modular design allows for quick replacement of worn parts.
- High Efficiency: Optimized internal geometry improves fluid dynamics and reduces energy loss.
FAQs
1. What is the function of a fluid end module in a mud pump?
The fluid end module is a critical component responsible for drawing in and discharging drilling fluid (mud) under high pressure during drilling operations. It houses key parts such as valve boxes, liners, pistons, and seals, which work together to maintain fluid flow and pressure stability. Its design directly impacts pump efficiency, durability, and resistance to abrasion from corrosive fluids
2. What materials are commonly used in fluid end modules for durability?
Fluid end modules and their components are typically constructed from high-strength alloys and wear-resistant materials, including:
- Hardened steel or chrome-plated surfaces for liners and pistons to withstand erosion 4.
- API-certified materials (e.g., API 5# valves) for critical parts like valve boxes, ensuring compliance with industry standards for pressure and performance 1.
- Isolation shrouds (e.g., in specialized designs) to enhance seal cooling and prevent fluid leakage, improving overall module lifespan
3. How do I select the right fluid end module for my mud pump model?
Key considerations include:
- Pump specifications: Match parameters like power rating (HP/KW), stroke length, and liner size to the module (e.g., a 500 HP pump may require a module with a max liner size of 6-3/4 inches) 1.
- Application requirements: For high-pressure drilling, prioritize modules with reinforced valve boxes and pressure ratings (e.g., 5000 psi outlet flanges) 1.
- Compatibility: Ensure parts are interchangeable with existing pump models (e.g., F series pumps like F1600/FB1600 or Gardner Denver PZ series)
4. What maintenance is required for fluid end modules?
- Regular inspection: Check for wear on liners, pistons, and valves; replace seals if leakage or pressure drops occur 3.
- Fluid circulation checks: Ensure cooling systems (e.g., isolation shrouds) are functioning to prevent overheating of seals 3.
- Compliance with warranty terms: Most modules offer a 1-year warranty for core components (e.g., gears), but require proper installation and maintenance
5. Are there common issues that cause fluid end module failures?
- Inadequate cooling: Poor fluid circulation around seals can lead to overheating and premature failure 3.
- Mismatched components: Using non-certified liners or valves may reduce pressure tolerance and cause catastrophic damage 1.
- Improper installation: Incorrect torque on flange connections or misalignment of stroke components can strain the module










We are here to answer your questions and support your needs.
