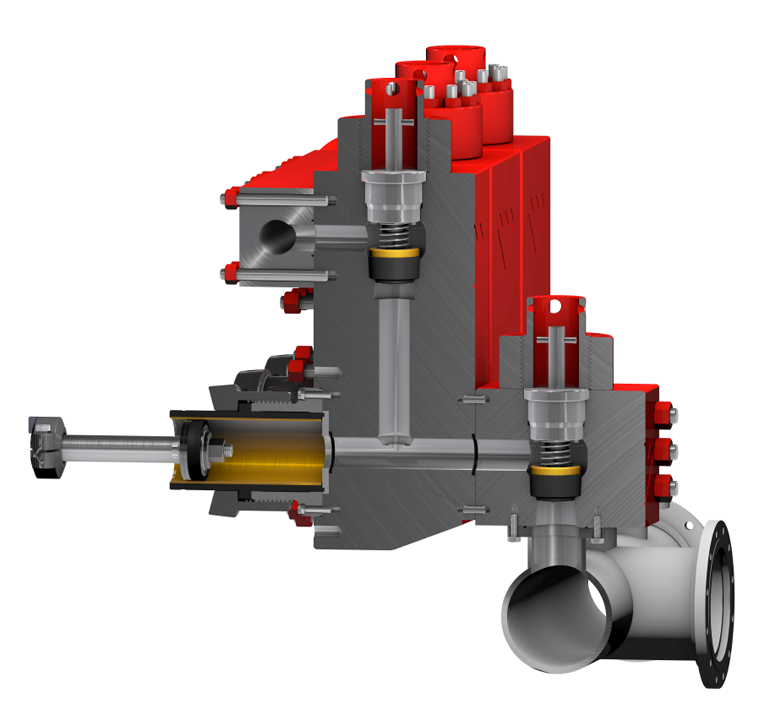
Piston and Liner System
The piston and liner system of a mud pump fluid end consist of the piston, liner, liner seal, wear plate, wear plate seal, liner retainer, the piston rods and rod clamps. Of these items, the piston will experience the most wear and will typically be replaced the most. Routine piston maintenance presents an excellent opportunity to inspect other components in the system.1) Please inspect if the rod clamp loosen which can cause damage to the rod that would affect its alignment with respect to the centerline of the liner bore, because any misalignment of this type would cause accelerated wear of the piston and liner.
2) Operators must know the properties of the drilling mud that is being used as well as the drilling conditions. If the mud temperature is more than 180 F, the operator needs to consider a piston that is designed for high-temperature service. Generally, urethane pistons do not perform as well when running in water-based muds as nitrile or hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber pistons. Conversely, nitrile pistons do not perform as well in oil-based muds as urethane pistons.
Valve and Seat System
The valve and seat system consists of the valve, valve seat, valve spring, valve guide and bushing, valve cover, and valve cover seal.1) Spring: is one of the most overlooked components of the fluid end.
If a valve runs for 500 hours at 100 strokes per minute, the spring will experience 3,000,000 cycles. Considering its high cycling function, the valve spring should be replaced with every valve replacement.
2) Valve seat: The full open valve seat has become more popular in recent years due to improved flow and ease of maintenance. In valve over valve fluid ends, the full open valve seat allows easy access to the suction valve without having to remove the discharge valve seat. This was previously not an option with webbed seat designs. However, webbed seats are easier and safer to remove from the module because of their design and anchor points with the removal tools.
3) valve guide bushing: another part that is often overlooked in the valve and seat system.
A worn or damaged valve guide bushing can cause the valve to stick or become misaligned and not engage the seat properly. This malfunction can lead to a module washout, a catastrophic failure of the module because of the high-pressure fluids.